How To Format Usb Flash Drive For Mac And Pc

Which File System Should You Use? Before you format your USB drive, you need to think about which file system to use. File Systems are simply ways of organising data on a storage device (such as hard drives or SD Cards), and support for various file systems varies depending on your operating system.
Windows 10 offers three file system options when formatting a USB drive: FAT32, NTFS and exFAT. Here is the breakdown of the pros and cons of each filesystem. Pros Cons Best Used For Fat 32 * Compatible with all major operating systems. * Less memory usage.
Word for mac double s. Once this is complete, launch the program and click on the '+' button at the top of the main window to import the PDF file you want to convert.
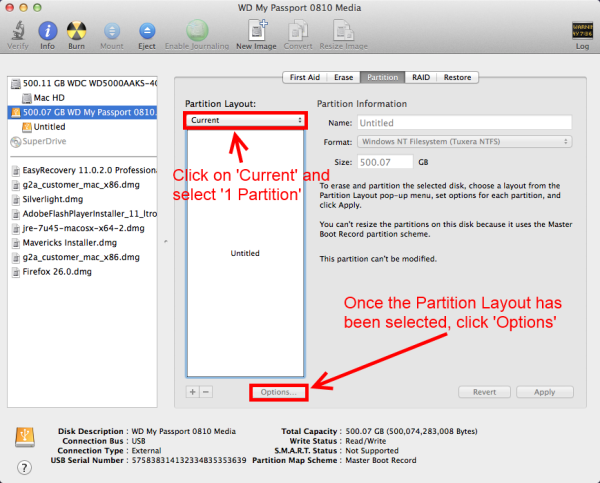
Formatting in context of USB or Hard Drives means deleting everything from that drive and rebuilding the file system so that we can use it with an Operating And here I will tell you two answers to this question that “How to Format USB on Mac?”. First, we will go with the straightforward way of doing it. Format flash drive in Exfat for transferring files between Mac and Pc. Read/Write FAT32 from both native Windows and native Mac OS X.
* Cannot handle single files larger 4GB. *Limited partition size (up to 32GB). * Removable storage devices such as USB Flash Drives. * Devices that need to be plugged into a variety of operating systems. NTFS * Can create partitions larger than 32GB.
Exc_bad_access word for mac. However, the problem of, still hasn’t been fixed in Office 2016 For Mac (or in Excel and PowerPoint for that matter). Some documents open fine but others end up with images and text all over the place and it remains to be seen whether this is a bug in the Office 2016 beta or a time bomb waiting to explode when users start to find that their old DOCX documents don’t open properly. On the plus side, clicking on links in Word is now much better – pages open instantly in your browser instead of having to wait around for ages as in Office 2011.
* Can read/write files larger than 4GB. * Supports on-the-fly file encryption. * Limited cross-platform compatibility. * Internal hard drives. * Windows system drives. ExFAT * Provides an unlimited file and partition size. * You may need to install drivers to get exFAT compatibility on Linux.
* External hard drives. * Flash drives if you want to work with files larger than 4GB. Now, let’s take a look at some ways you can format your USB drive on Windows 10. Method 1: Format USB Drive using File Explorer This is the easiest way and simply requires you to plug in your USB Drive, open the Windows File Explorer and right click your drive to view a number of actions that you can perform. Clicking the “format” option will open a new window where you can configure the available options before formating your drive. I will be going with the NTFS file system because I need cross-platform compatibility (Windows and Linux), and I may need to transfer files larger than 4GB on occasion.
As for allocation size, it all depends on what you want to do with your drive. If you have a large drive (such as a 500GB hard drive), a large allocation size such as 32 kilobytes will make your device faster, but storage space may fill up quicker. For small drives, such as 4GB or 8GB flash drives, a smaller allocation size will help conserve space. I’m going with 4kb (4096 bytes) as my allocation size because I work with small files most of the time, and my flash drive is just 16GB. The volume label is simply the name of your USB Drive. You can name your drive anything you want.
Once you have selected the options, you can click the format button to begin the formatting process. Ticking the “Quick Format” checkbox means that your drive will not be scanned for bad sectors. If you have a malfunctioning drive, you might want to uncheck that box for a more thorough scanning.